Day 1 :
Keynote Forum
Louis Samuels
Thomas Jefferson University,USA
Keynote: Pump-Assisted Beating-Heart Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting: Application and Advantages

Biography:
Louis Samuels is professor surgery at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia Pennsylvania. His Medical School, General Surgery and Cardiothoracic Surgery training were completed at Hahnemann University in Philadelphia Pennsylvania. Dr. Samuels has published over 100 peer-reviewed manuscripts on a variety of topics in Cardiothoracic Surgery, most notably in the field of artificial heart technologies and the management of acute and chronic heart failure. In the past fifteen years, Dr. Samuels has also taken interest in Beating Heart Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) and has performed over 1000 of these procedures including totally off-pump (i.e. OP-CAB) and Pump-Assisted CABG (i.e. PAD-CAB). Dr. Samuels maintains a busy clinical practice and continues to be involved with clinical research as well as serving on various committees related to the oversight of ongoing and prospective clinical trials
Abstract:
BACKGROUND: The techniques utilized to accomplish Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) include the traditional use of cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) with aortic cross-clamping and cardioplegic arrest to totally Off-Pump (i.e. OP-CAB) without CPB. The purpose of this report is to describe a hybrid approach—Pump-Assisted Direct CABG (PAD-CAB)-- with the aid of CPB without aortic cross-clamping and cardioplegic arrest.
METHODS: Between November 2003 and December 2016, 317 PAD-CAB procedures were performed by the author/surgeon. The PAD-CAB procedures were achieved with standard CPB via sternotomy under normothermic conditions with the mean arterial pressures (MAP) kept between 60 and 80 mmHg. Outcome measures included hospital mortality and specific major adverse events (MAE) benchmarked against the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) database. The number of bypass grafts, status of the case, specific patient factors, and postoperative length of stay (LOS) were also assessed.
RESULTS: There were 238 male (75%) and 79 (25%) female patients. The mean age was 67 years (range: 38 to 92 years). The mean ejection fraction (EF) was 50% (range: 0 to 75%) with 66 cases (21%) having an EF < 40%. Two hundred seventy-seven cases (87.4%) were non-emergent with forty cases (12.6%) classified as emergent/salvage. The average of number of bypass grafts was 3.24 (range: 1 to 5). The postoperative LOS averaged 7.5 days with a median of 6 days. There were two hospital deaths (0.65%). Major Adverse Events were: 1 deep SWI (0.32%), 3 CVAs (0.95%), and 5 POBs (1.58%).
CONCLUSIONS: PAD-CAB is a safe and effective operation with outcomes that are equivalent or superior to the outcomes reported in the STS registry for CABG. The PAD-CAB technique takes advantage of the circulatory stability achieved with CPB assistance and eliminates the potential risks associated with aortic cross-clamping and cardioplegic arrest.
Keynote Forum
Miguel Guillermo Garber
Garber,Spanish Society of Regenerative Medicine and Cell Therapy (SEMERETEC), Spain
Keynote: Regeneration and repair in cardiovascular disease, obstacles and opportunities

Biography:
Garber has over 32 years of experience in Internal Medicine and Cardiology, in addition to training, research, and development expertise in Regenerative Medicine. Over the past 12 years, he has made a significant contribution to stem cell research, specializing in the exploration and development of stem cell therapies for cardiac disorders, osteoarthritis, and neurological and autoimmune diseases. Formerly the Director of American Medical Information Group, he now serves as the Medical Director of Regenerative Medicine Madrid and the President of the Spanish Society of Regenerative Medicine and Cell Therapy (SEMERETEC). He also teaches a Master’s degree program in Regenerative Medicine and edits a number of scholarly journals on the subject.
Abstract:
The primary cause of death among chronic diseases worldwide is ischemic cardiovascular diseases, such as stroke and myocardial infarction. Recent evidence indicates that adult Mesenchymal stem cells therapy aimed at restoring organ function, and cardiovascular repair represent promising strategies to treat cardiovascular diseases, and have been recognized as one of the potential therapeutic agents, following several tests in animal models and clinical trials. In the process, various sources of mesenchymal stem cells have been identified which help in cardiac regeneration by either revitalizing the cardiac stem cells or revascularizing the heart. Although mesenchymal cell therapy has achieved considerable admiration and promising therapeutic strategy is the priming of therapeutic MSCs with stem cell modulators before transplantation. therapeutic efficacy of MSCs in vitro or in vivo from cell priming to tissue engineering strategies, for use
some challenges still remain that need to be overcome in order to establish it as a successful technique, questions going on: Which specific types of stem cells are likely to be most effective?, Can heart cells divide, and, if so, can we develop strategies to stimulate the growth and differentiation of the cardiac cells left in the injured heart to promote recovery of tissue mass and function?
Nobody knows at the time being what will be the best therapy for our patients.”,“We may need different cells for different patients and different cells for drug discovery or tissue engineering.” Which cell(s) will ultimately prove to be useful in patients is a matter of opinion.
1.Bergmann O, et al. (2009) Evidence for cardiomyocyte renewal in humans. Science 324(5923):98-102.
2.Friedenstein AJ, et al. (1974)
3.Precursors for fibroblasts in different populations of hematopoietic cells as detected by the in vitro colony assay method. Exp Hematol 2(2):83-92.
4.Pittenger MF, et al. (1999) Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 284(5411):143-147.
5.Sekiya I, Vuoristo JT, Larson BL, & Prockop DJ (2002) In vitro cartilage formation by human adult stem cells from bone marrow stroma defines the sequence of cellular and molecular events during chondrogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99(7):4397-4402.
6.Wagner W, et al. (2005) Comparative characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood. Exp Hematol 33(11):1402-1416.
7.Rasmusson I (2006) Immune modulation by mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Cell Res 312(12):2169-2179.
8.Arminan A, et al. (2010) Mesenchymal stem cells provide better results than hematopoietic precursors for the treatment of myocardial infarction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 55(20):2244-2253.
9.Gnecchi M, et al. (2005) Paracrine action accounts for marked protection of ischemic heart by Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cells. Nat Med 11(4):367-368.
10.Pillai RS (2005) MicroRNA function: multiple mechanisms for a tiny RNA? Rna 11(12):1753-1761.
11.Zhao Y & Srivastava D (2007) A developmental view of microRNA function. Trends in biochemical sciences 32(4):189-197.
12.Eulalio A, et al. (2007) Target-specific requirements for enhancers of decapping in miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Genes Dev 21(20):2558-2570.
13.Small EM & Olson EN (2011) Pervasive roles of microRNAs in cardiovascular biology. Nature 469(7330):336-342.
14.Matkovich SJ, et al. (2009) Reciprocal regulation of myocardial microRNAs and messenger RNA in human cardiomyopathy and reversal of the microRNA signature by biomechanical support. Circulation 119(9):1263-1271.
15. Sanina C., Hare J. M. Mesenchymal stem cells as a biological drug for heart disease: where are we with cardiac cell-based therapy? Circulation Research. 2015;117(3):229–233. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.117.306309
16.62. Squillaro T., Peluso G., Galderisi U. Clinical trials with mesenchymal stem cells: an update. Cell Transplantation. 2016;25(5):829–848. doi: 10.3727/096368915x689622
Keynote Forum
Guy Hugues Fontaine
Université Pierre et Marie Curie, France
Keynote: Mechanism of Torsades de Pointes elucidated in human AV block

Biography:
Guy Fontaine has made 15 original contributions at the inception of cardiac pacemakers in the mid-60s. He has published more than 900 scientific papers including 201 book chapters. He is included in the Profiles in Cardiology (W Hurst 2003) book of the 216 individuals who have made a significant contribution to the study of cardiovascular diseases since the 14th century. He has been included in the book “500 greatest Geniuses of the 21st century” of the American Biographical Institute (ABI 2005). He was the reviewer of 17 journals both in clinical and basic Science. He served during 5 years as a Member of the Editorial Board of Circulation. He has been invited to give 11 master lectures of 90 minutes each during three weeks in the top universities of China (2014).
Abstract:
Two successive mechanisms may explain Torsades de Pointes (TdP) in patients with complete AV block. (1) A phase 2 reentrant phenomena in adjacent side-to-side myocardial fibers based on dispersion of action potential duration to explain the first TdP beat (2) this phenomenon is followed by a fast circus movement reentry in agreement with the “leading circle” concept with a speed only limited by the ventricular refractory period. The initiation of multiple “rotors” may result in VF because long episodes may lead to myocardial ischemia (Fig.1). However, intraventricular myocardial conduction blocks may explain that most TdPs stop spontaneously. Because this phenomenon needs a thin myocardial structure as demonstrated by optical mapping we suspect that its origin is located in the “crista supraventricularis”. Two exit sites of the circus movement can take place along the antero-superior and postero-inferior sulcia explaining the opposite orientation of the initial vectors observed at the beginning of most of the torsades. This is followed by a Wenkebach phenomenon on at least one of these two pathways. This may explain the feature of the twisting of the QRS tips around the isoelectric line. This theory is comforted by the abrupt change in the direction of activation suggesting a Mobitz type 2 block occurring on one of these two preferential pathways. The same mechanism can be observed on a reentrant loop around an anatomical obstacle producing a TdP-like arrhythmia in case of two exit sites of opposite directions
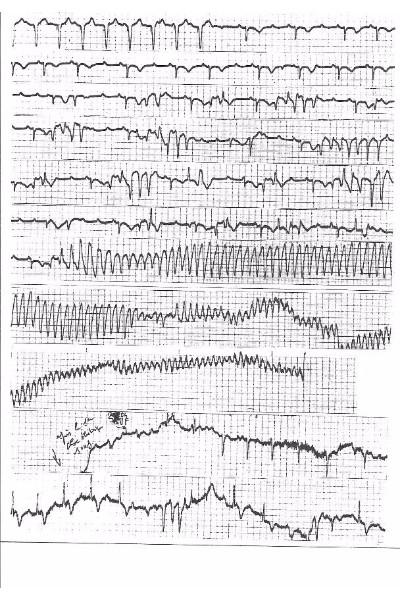
- Clinical Cardiology | Heart Diseases & Heart Failure | Cardiac Surgery | Clinical Case Reports on Cardiology
Session Introduction
John Kassotis
Columbia University, USA
Title: Current Concepts in the Treatment of Sudden Cardiac Death

Biography:
John Kassotis, MD is a practicing Cardiac Electrophysiologist in Brooklyn, NY. He graduated from Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons in 1990 and has been in practice for 26 years. He completed a residency at Columbia Hospital. He is also specializes in Cardiology (Cardiovascular Disease) and Internal Medicine. He currently practices at Division of Cardiovascular Medicine EP Section and is affiliated with Lutheran Medical Center and SUNY Downstate Medical Center University Hospital of Brooklyn. He is board certified in internal medicine, cardiovascular disease, clinical cardiac electrophysiology, and advanced heart failure and transplant. He is a member of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers, the American College of Physicians, the American Society of Angiology, and the American Society of Sleep Medicine
Abstract:
Sudden Cardiac Death remains a significant public health concern. With approximately 400,000 cases in the US alone, the incidence is higher than death associated with breast cancer, traffic accidents and other more commonly published disease states. Despite significant advances, the incidence of sudden cardiac death remains high. With greater public awareness, ease of access to defibrillators (e.g. AEDs) we are hopeful that there will be a significant impact in reducing morbidity and mortality. However, the most significant impact will be derived from focusing our attention on identifying and managing patient’s known to have a predisposition for SCD, pre-event. With improvements in technology and refinements in implantation techniques, the placement of implantable cardioverter defibrillator, has emerged as the standard of care for primary and secondary prevention. The purpose of this review will be to acquaint the audience to better identification of patient’s at high risk for SCD, diagnostic and therapeutic interventions as well as, future initiatives.
Salah A. Mohamed
UKSH-Campus Luebeck, Germany
Title: Genetic basis, pathogenesis, and haemodynamic aneurysm of the ascending aorta in patients with a bicuspid aortic valve

Biography:
Salah A. Mohamed has his expertise in evaluation and passion in improving the health and wellbeing. Since 2002 he is working as laboratory and group leader in the Department of Cardiac and Thoracic Vascular Surgery, Luebeck, Germany. He is an Associate Professor in molecular biology/cardiac surgery at the University of UKSH-Campus Luebeck, Germany. His research has included â— cardiovascular disease (e.g. Genetic Etiology and Molecular), â— Epidemiology of aortic and aortic valve disease, â— Evaluation and Validation of Drugs and Biomarkers, and â— aging of the heart. His Laboratory also focuses on understanding the causes of atrial fibrillation investigating.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: The normal diameter of the aorta in adults is approximately 35 mm. A vessel bulge (aneurysm) is defined as permanent and exceeding of the standard value involving all layers of the vessel wall. Aneurysm of the ascending aorta is responsible for 1–2% of all deaths in industrialized countries. In approximately 50% of patients with a bicuspid aortic valve (BAV), the most common congenital heart disease, aneurysms of any or all segments of the aorta occurs. While aortic aneurysms are generally a benign condition, a consistent increase in the diameter of an aneurysm can give rise to catastrophic events such as acute aortic dissection (AAD) or aortic rupture. Methodology & Research orientation: Comprehensive genetic, molecular analysis and proteomic approaches to understand complex cellular processes and networks in the pathophysiology of aneurysms of the ascending aorta. To support two known kinds of hypotheses proposed to explain the causality in aneurysms formation, intrinsic factor is further investigated and analyzed in sense of vascular remodeling between congenital BAV and Marfan’s patients (MFS). In MFS, mutations in the gene encoding for the extracellular matrix protein fibrillin-1 can be observed; this mutations lead to dysregulation of the transforming growth factor-beta signaling. Findings: The interaction between mechanical forces and biological function is intimately coupled. In the subsequent molecular investigations of AAD, further genes were described, and their proteins were altered in patients with AAD. Conclusion & Significance: The etiology of BAV and the thoracic aortic aneurysm appears to be multiple. At the onset of valvulogenesis a number of mechanisms [e.g. Genes, epigenetic factors, fluid forces (Fig)] may be involved, either alone or combined, in the pathogenesis.
Fig. Genetic basis and pathogenesis of BAV/BAV associated aortopathy
1. Navarrete Santos et al., (2016). Collagen analysis of the ascending aortic dilatation associated with bicuspid aortic valve disease compared with tricuspid aortic valve. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2016;5:1-6
2. Lazar-Karsten et al., (2016). Generation and Characterization of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Lines Derived from a Patient with a Bicuspid Aortic Valve.
3. Paloschi et al., (2015). Aneurysm Development in Patients With a Bicuspid Aortic Valve Is Not Associated With Transforming Growth Factor-ß Activation. ATVBAHA 2015
4. Mohamed et al., (2006). Novel missense mutations (Thr595Met and Pro1795His) in NOTCH1 in patients with bicuspid aortic valve. BBRC. 2006;345:1460-146
5. Mohamed et al., (2005). Ubiquitin fusion degradation 1-like gene dysregulation in Bicuspid Aortic Valve. J Thorac Cardiovas Sur; 2005;130:1531-1536
Lobina Kaniz Kalam
Albert Einstein College of Medicine, USA
Title: Regression of Atherosclerosis: a study of statins vs. low calorie high anti-inflammatory diet

Biography:
Lobina Kaniz Kalam is an Assistant Professor of Medicine at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Montefiore, Bronx, NY. I have a Distinguished Fellowship in Cardiology from The American Academy of Cardiology, 2007. I am a self-published poet and oil painter.
Abstract:
1)Statement of the problem: There is a decrease in morbidity and mortality from the use of Statin drugs for known Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) as well as those without clinical evidence of CAD. Regression of atherosclerotic plaque occurs after lipid lowering begins. This can best be characterized through intra-coronary or Carotid ultrasonography. Using statins alone, studies have shown plaque regression occur earliest at 12 months. Furthermore, chronic inflammation plays a part in multiple unstable plaques in different coronary arteries.
2)Methodology and Theoretical Orientation: A randomized controlled study on 1500 patients over 12 months with Inclusion criteria of hyperlipidemia, and known coronary or carotid atherosclerosis. Statin arm: Zocor 20, and 40 mg, 80mg and usual American diet.
Low-Calorie diet arm meal plan: breakfast will be three eggs any way with any Vegetables. Lunch will be the Detox juice (which I myself have tried for 6 months with incredible outcomes for both BMI and Lipids), with three Red Apples, 1 cup Spinach, 1 cup Kale, 1 cup Celery. Dinner will be 1 cup brown rice, 1 cup any meat cooked anyway, 1 cup vegetables.
3) Findings: This study will take 1 year of dedicated research for data collection. Outcomes to be studied will be a) LDL b) HDL c) TG d) BMI e) CRP f) carotid and coronary vessel wall thickness.
4) Conclusion and Significance: Hypothesis of study: A low calorie-high anti inflammatory diet as the Detox juice diet plan, may be as effective as Statins in regression of Atherosclerotic plaque.
Recent publications:
Last publication was in basic science on Xenopus developmental genetics.
M. Parvaiz Farshori
College of Medicine University of Hail, Saudi Arabia.
Title: Blood group antigen (ABO and Rh) distribution in Myocardial Infarction (MCI) Patients of Hail region in Saudi Arabia
Biography:
To be Updated Soon..
Abstract:
Blood group antigen (ABO and Rh) distribution in Myocardial Infarction (MCI) Patients of Hail region in Saudi Arabia. M.Parvaiz. Farshori (supervisor).
M. Parvaiz Farshori*, Yaser Ghareeb Ibrahim Alrashdan , Abdulmmajeed Hamoud M Alshammari, Raiya Khaled Ali AlTamimi, Hayam Abdullah Houmood Alshammari, Abrar Hamad Saleh Alageel, Fayez Ammar S. Alshammari.
*Department of Physiology, College of Medicine University of Hail, Saudi Arabia.
Introduction: According to WHO 2014 world health ranking survey Saudi Arabia ranks 27th in coronary heart disease (CHD) related deaths. According to the same survey CHD was also the leading cause of deaths in Saudi Arabia followed by stroke, influenza, diabetes, and the kidney disease (WHO, 2014 survey).
Several studies have suggested relationship between inheritance of blood group antigens and certain diseases such as diabetes (Farshori et al, 2016, 2017, Fagherazzi et al, 2015, Meo et al 2016), cardio vascular disease (Saima et al, 2015, Chen et al. 2016) and cancers (Zhang et al, 2015). Although many studies have suggested an association between the blood groups and the cardiovascular diseases however results have been inconsistent. For example one study suggests an association between the O blood groups and the increased risks of coronary heart disease Biswas et al., 2013, while others show blood group A to be associated with an increased risk CHD (Chen et al., 2016).
Aim: Since there are different studies with different conclusions about the association between CAD and the inheritance of AB and Rh (D) antigens, and since it is the leading cause of death in Saudi Arabia, we decided to perform a small study on 120 CHD patients who have had an acute myocardial infarction (MCI) in the recent past and were admitted to king Khaled hospital (KKH) in Hail region of Saudi Arabia.
Materials and Methods: This study included 329 control and 111male myocardial infarction patients enrolled at (KKH) Cardiology Department in Hail region of Saudi Arabia. On these patients’ ABO data was collected along with some other risk factors such as diabetes, smoking habits, age, gender, obesity and the family history of CAD. Data was statistically analyzed using Z- test for two population proportions.
Results: Out of 329 control male population (age range 12-86, mean age 32.7 years), 3.35% were A- and 20.7% were A+, 3.95% were B- and 14.28% were B+, 2.43% were AB- and 8.2% were AB+, 8.5% were O- and 38.3% were O+. In comparison when we analyzed the blood group distribution among patients with myocardial infarction (age range 16-90, mean age 49.4 years), we found: Out of 111 male patients 0.9% were A- and 30.6% were A+, 1.8% were B- and 18.01% were B+, 0.9% were AB- and 6.3% were AB+, 0.9% were O- and 40.5.3% were O+.
Conclusions: As compared to control group A+ male patient show statistically high incidences of MCI and O- show significantly low incidences of MCI.
References:
Bai-Lin Zhang, Na He, Yu-Bei Huang, Feng-Ju Song, Ke-Xin Chen. 2015. ABO blood groups and Risk of Cancer: A systematic review and meta analysis. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention. 15: 11, 4643-50.
John Kassotis
Columbia University, USA
Title: Current concepts in the treatment of sudden cardiac death

Biography:
John Kassotis, is a practicing Cardiac Electrophysiologist in Brooklyn, NY. He graduated from Columbia University College of Physicians and Surgeons in 1990 and has been in practice for 26 years. He completed a residency at Columbia Hospital. He is also specializes in Cardiology (Cardiovascular Disease) and Internal Medicine. He currently practices at Division of Cardiovascular Medicine EP Section and is affiliated with Lutheran Medical Center and SUNY Downstate Medical Center University Hospital of Brooklyn. He is board certified in internal medicine, cardiovascular disease, clinical cardiac electrophysiology, and advanced heart failure and transplant. He is a member of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers, the American College of Physicians, the American Society of Angiology, and the American Society of Sleep Medicine.
Abstract:
Sudden Cardiac Death remains a significant public health concern. With approximately 400,000 cases in the US alone, the incidence is higher than death associated with breast cancer, traffic accidents and other more commonly published disease states. Despite significant advances, the incidence of sudden cardiac death remains high. With greater public awareness, ease of access to defibrillators (e.g. AEDs) we are hopeful that there will be a significant impact in reducing morbidity and mortality. However, the most significant impact will be derived from focusing our attention on identifying and managing patient’s known to have a predisposition for SCD, pre-event. With improvements in technology and refinements in implantation techniques, the placement of implantable cardioverter defibrillator, has emerged as the standard of care for primary and secondary prevention. The purpose of this review will be to acquaint the audience to better identification of patient’s at high risk for SCD, diagnostic and therapeutic interventions as well as, future initiatives.
Christine Gasperetti
Christine Gasperetti, University of Pennsylvania Health System, USA
Title: Hemodynamic Concepts Important to Protected PCI
Biography:
Christine Gasperetti is an interventional cardiologist with interests in high risk and protected coronary intervention as well as acute myocardial infarction. She has been involved in many studies of coronary artery disease and determinants of platelet function during coronary intervention. She is affiliated with the University of Pennsylvania Health System and works at several of their hospitals and affiliates
Abstract:
With advancements in cardiac technology, it has now become possible to offer patients with complex and high-risk coronary artery disease, including those with cardiogenic shock (CGS) revascularization with percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). Such patients often require hemodynamic support and are the procedure is thus termed "protected PCI". Protected PCI has led to breakthrough in the survival ceiling for patients presenting with CGS complicating acute myocardial infarction (Ml) and to redefinition of protocols with which to best offer PCI in the setting of CGS. Ultimately, use of varying support models may lead to improved understanding of the components of shock states in ischemia and infarction.
The presentation includes two patients who required high risk PCI in the setting of CGS. The first patient presented with Inferior Ml complicated by RV infarction and was supported with RV Assist Device
(RVAD). The second patient presented with cardiac arrest during Anterior Ml and underwent emergent PCI with limited support in the off-site cardiac catheterization laboratory setting.
Following these presentations, an introduction to analysis of hemodynamics of support using the Harvi model developed by Daniel Burkhoff, MD PhD and colleagues will be given and used to illustrate important hemodynamic concepts in ventricular supfjort including changes in cardiac power, uncoupling of systemic and LV pressures, changes in contractility and coronary perfusion pressure, and comparison of devices used.
References
1. Burkhoff D, Sayer G, Doshi D, et al. (2015) Hemodynamics of Mechanical Circulatory Support.
JACC Vol. 66. No. 23. 2015 2663-74.
2. Burkhoff, D, Naidu SS (2012) The science behind percutaneous hemodynamic support: review
and comparison of support strategies. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions. Vol. 80.
No. 5. 2012. 816-29.
3. Kapur NK, Qias X, Parchuri V, et al. (2015) Mechanical Pre-Conditioning With Acute Circulatory
Support Before Reperfusion Limits Infarct Size in Acute Myocardial Infarction. JACC Heart Failure
(2015) Vol. 3. No. 11. 2015. 873-82.
4. Napp LC, Kuh C, Bauersachs J. (2017) ECMO in cardiac arrest and cardiogenic shock. Herz 2017:
vol. 42. 27-44.
5. O'Neill W, Basir M, Dixon S, et al. (2017) Feasibility of Early Mechanical Support During
Mechanical Reperfusion of Acute Myocardial Infarct Cardiogenic Shock. JACC Vol. 10. No. 6.
2017 624-5.
6. Rihal CS, Naidu SS, Givertz MM, et al. (2015) 2015 SCAI/ACC/HFSA/STS Clinical Expert Consensus
Statement on the Use of Percutaneous Mechanical Circulatory Support Devices in
Cardiovascular Care. JACC Vol. 65. No.l9. 2015 e7-e26.
Ajeya N Ukadgaonkar
Poona Hospital and Research Centre, India
Title: A giant coronary artery aneurysm burrowing into left ventricular cavity following drug eluting stent implantation: A case report

Biography:
Ajeya N Ukadgaonkar is pursuing a superspeciality course (DNB) in Cardiology in Poona Hospital and Research Centre, India. He has completed his MD in Internal Medicine and has worked as an assistant professor in Internal Medicine. He has 2 publications in international and 1 publication in a national journal to his name. He bears a special interest in the field of research.
Abstract:
Coronary artery aneurysms are rarely seen with an overall incidence of 1.5 to 5% and post coronary intervention incidence is 0.2 to 1.7%. They are reported to be more common after a drug eluting stent (DES) rather than a bare metal stent (BMS). Post stent coronary artery aneurysm formation is a dreaded complication which can lead to sudden death. We report a case of a 53 years old diabetic and hypertensive male who underwent percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA) to the left anterior descending artery (LAD) with everolimus eluting stent (EES). Two months later he presented with angina, heart failure and severe left ventricular dysfunction. His check coronary angiography revealed a giant (30 x 20 mm) type 2 coronary artery aneurysm arising from LAD with occluded stent distal to the aneurysm. He was posted for surgery, during which the aneurysm was found to be communicating directly to the left ventricular cavity. Surgical aneurysmectomy with coronary artery bypass graft to LAD was done. Post operatively, the patient recovered rapidly and was discharged. To the best of our knowledge, acquired (post PTCA) giant coronary artery aneurysm communicating to the left ventricular cavity has hardly been reported yet. Due to paucity of these types of cases we have a limited experience in diagnosis and management of these patients. This case report will serve as an informative tool for diagnosis and management of these rare presentations of the heterogeneous disease. Prompt identification and treatment is the key for management of this fatal complication.
Recent Publications
1. Gadepalli R et al (2017) A case of early development of giant coronary artery aneurysms after drug-eluting stents implantation: An unpredictable menace. Interventional Medicine & Applied Science, Vol. 9 (1), pp. 47–50.
2. Kar et al (2016) Post Balloon Stent Right Coronary Artery Aneurysm: Cardiologist’s Nightmare. J Cardiovasc Dis Diagn 2016, S1.
3. Bhupali et al (2015) Giant Coronary Artery Pseudoaneurysm after Drug-Eluting Stent Implantation. International Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2015, 6, 554-560.
4. Mishra et al (2014) Multiple Giant Coronary Arterial Aneurysms following Sirolimus Drug Eluting Stents Implantation. Journal of the association of physicians of india vol 62 october, 2014.
5. Crawley PD, Mahlow WJ, Huntsinger DR, Aï¬niwala S, Wortham DC (2014) : Giant coronary artery aneurysms: Review and update. Tex Heart Inst J 41, 603–608.
6. Kadakia MB, EppsKC, JulienME, OgbaraJ, Giri J, KolanskyDM, Woo YJ, Wilensky RL (2014) : Early aneurysm formation after everolimus eluting stent implantation. Circ Cardiovasc Interv 7, 266–267.
7. Bennett J, Dubois C (2013) : A novel platinum chromium everolimus eluting stent for the treatment of coronary artery disease. Biologics 7, 149–159.
8. Marla R, Ebel R, Crosby M, Almassi GH (2009): Multiple giant coronary artery aneurysms. Tex Heart Inst J 36, 244.
9. Pahlavan PS, Niroomand F (2006) : Coronary artery aneurysm: A review. Clin Cardiol 29, 439–443
Claudia Montanaro
Royal Brompton Hospital, London, UK
Title: Cardiovascular risk in adolescents and exercise issues in the congenital heart disease population.

Biography:
Claudia Montanaro is a Cardiologist with an interest in Congenital Heart Disease and Cardiac Imaging. She currently is a fellow at Royal Brompton Hospital in London, UK. She trained at the Hospital San Raffaele in Milan, Italy. She is board certified in adult congenital heart disease echo (ESC). Her academic interests include outcome analysis in patients with congenital heart disease (in particular pulmonary atresia and ventricular septal defect) as well as 3D-CMR reconstruction of complex heart lesion. Her innovative research, supported by the Italian Society of Cardiology, is directed into the non-invasive detection of atrial fibrosis. Dr. Montanaro is a member of the editorial board of The International Journal of Cardiology. She is co-author of manuscripts published in peer review journals and book chapters focused on congenital heart disease and heart failure.
Abstract:
In 2009 in the European Union the costs related to cardiovascular diseases amounted to E106 billion, representing ~9% of the total expenditure on healthcare[i]. The scientific community has allocated significant funds to identify behaviour in the young which might adversely affect health in adult life. Based on the American Heart Association guidelines, the ideal cardiovascular health(iCVH) construct[ii] consists of 4 ideal health behaviors (nonsmoking, BMI <25 kg/m2, physical activity at goal level, and diet consistent with current recommendations) and 3 ideal health factors (untreated total cholesterol <200 mg/dL, untreated BP <120/<80 mmHg, and untreated fasting glucose <100 mg/dL). Adolescents from a high socio-economic class are more likely to have a healthy diet, high levels of physical fitness and consequently lower cardiovascular risk[iii]. Only 47% of U.S. adolescents and 54% of European adolescents exhibit at least 5 of the 7 iCVH components[iv] [v]. Scientific literature shows that psychological and biological factors, social environment and community settings play an important role in the adolescent’s habits. Healthy habits and good physical activity is paramount for these patients. In the past, all patients with CHD were excluded from competitive sports mainly because of the risk of sudden death (SD). It has been noted that sudden death in CHD patients is generally rare. Aerobic activity and sport in general should always be recommended; there are exceptions as patients with severe left and/or right outflow tract obstructions, failing Senning or Mustard repairs, severe pulmonary hypertension, bicuspid aortic valve with severe aortic dilation and particular cases of anomalous coronary artery, in which it is reasonable to discourage competitive sports. Nowadays, available tools to estimate the risk of SD are appropriate interpretation of ECG, fibrosis evaluation with cardiac magnetic resonance and cardiopulmonary exercise test.
Patients with congenital heart disease should be cared for in a tertiary centre where high level of expertise and knowledge informs any ad hoc counselling based on objective and self-perceived patient capacity and potentiality
[i] 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts) European Heart Journal (2016) 37, 2315–2381
[ii] Lloyd-Jones DM, Hong Y, Labarthe D et al. Defining and setting national goals for
cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: the American Heart Association's
strategic Impact Goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation. 2010;121:586-613.
[iv] Shay CM, Ning H, Daniels SR, Rooks CR, Gidding SS, Lloyd-Jones DM. Status of cardiovascular health in US adolescents: prevalence estimates from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) 2005-2010. Circulation. 2013;127:1369-76.
[v] Pontus Henriksson, Hanna Henriksson, Luis Gracia-Marco, Idoia Labayen, Francisco B Ortega, Inge Huybrechts, Vanesa España-Romero, Yannis Manios, Kurt Widhalm, Jean Dallongeville, Marcela Gonzalez-Gross, Ascension Marcos, Luis A Moreno, Manuel J Castillo, Jonatan R Ruiz, on behalf of the HELENA study group3Prevalence of ideal cardiovascular health in European adolescents: The HELENA Study
[1] 2016 European Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice (The Sixth Joint Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology and Other Societies on Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in Clinical Practice (constituted by representatives of 10 societies and by invited experts) European Heart Journal (2016) 37, 2315–2381
[1] Lloyd-Jones DM, Hong Y, Labarthe D et al. Defining and setting national goals for cardiovascular health promotion and disease reduction: the American Heart Association's strategic Impact Goal through 2020 and beyond. Circulation. 2010;121:586-613.
[1] Shay CM, Ning H, Daniels SR, Rooks CR, Gidding SS, Lloyd-Jones DM. Status of cardiovascular health in US adolescents: prevalence estimates from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) 2005-2010. Circulation. 2013;127:1369-76.
[1] Pontus Henriksson, Hanna Henriksson, Luis Gracia-Marco, Idoia Labayen, Francisco B Ortega, Inge Huybrechts, Vanesa España-Romero, Yannis Manios, Kurt Widhalm, Jean Dallongeville, Marcela Gonzalez-Gross, Ascension Marcos, Luis A Moreno, Manuel J Castillo, Jonatan R Ruiz, on behalf of the HELENA study group3Prevalence of ideal cardiovascular health in European adolescents: The HELENA Study

Biography:
Heba Kamal Weshahy, assistant lecturer of pediatrics and pediatric cardiology in National Heart Institute, Egypt. She has M.B.B.Ch degree in medicine in December 2004- Cairo University, Master degree in pediatrics and neonatology in August 2009- Cairo University, studying MD degree in pediatrics and pediatric cardiology- Cairo University. She has about 12 years experience in pediatric cardiology, multislice CT angiography, pediatric echocardiography, pediatric diagnostic and interventional catheterization, medical and surgical pediatric cardiac intensive care unit and congenital cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. She did about 2000 multislice CT angiography for cases of congenital heart diseases of the heart and blood vessels, about 4000 echocardiography for cases of congenital heart diseases, about 100 interventional catheterization for cases of congenital heart diseases and about 50 diagnostic catheterization for cases of congenital heart diseases
Abstract:
1-(Dilated cariomyopathy in a four years old girl):
Clinical picture: dysnea, respiratory distress, cardiomegaly and gallop.
Echocardiography: dilated left ventricle with impaired contractility EF 20%, FS 10%.
CT angiography
Absent left main coronary artery.
Anomalous origin of the LCX and LAD by separate ostia from the left side of the main pulmonary artery.
Diffuse dilatation of the RCA.
Many dilated intercoronary collaterals.
Conclusion: adult type of ALCAPA.
2-(Dilated cardiomyopathy in a ten months old girl):
Clinically: dysnea, recurrent pneumonia, respiratory distress, cardiomegaly and gallop.
Echocardiography: dilated left ventricle with impaired contractility EF 22%, FS 10%, suspected ALCAPA.
CT:
Anomalous origin of the LAD from the left side of the main pulmonary artery.
The left circumflex arises from the left coronary sinus of Valsalva and runs its normal course.
Mild diffuse dilatation of the RCA.
Conclusion: ALCAPA.
3-(ASD with severe pulmonary hypertension):
Clinically: 9 months old female, recurrent pneumonia, feeding difficulties, poor weight gain, cardiomegaly and accentuated S2.
Echocardiography: dilated RV, severe TR, moderate sized secundum ASD and pulmonary hypertension.
CT:
Average sized main pulmonary artery continuous with its left branch.
Absent right pulmonary artery.
Indirect MAPCA supplying the right lung.
Diminished right lung volume.
4-(Tetralogy of Fallot with upper limb weakness):
Clinically: 20 months old female, dysnea, cyanosis, left upper limb weakness, and systolic murmur.
Echocardiography: TOF.
CT:
Average sized confluent main pulmonary artery and its both branches.
Abnormal origin of the left subclavian artery from the left pulmonary artery.
Right sided aortic arch.
5-(Postoperative Residual VSD):
Clinically: 18 months old female, 6 months following surgical closure of VSD and epicardial pacemaker insertion, dysnea, respiratory distress, pansystolic murmur.
Echocardiography: abnormal flow directed from the aorta to the RV, suspected ruptured sinus of Valsalva.
CT :
Residual VSD between the LVOT and RV cavity just below the Tricuspid valve.
Recent publications:
1-Weinberg PM, Natarajan S, Rogers LS. (2013) Aortic arch and vascular anomalies.
2-Uchino A, Saito N, Okada Y, et al.(2013) Variation of the origin of the left common carotid artery diagnosed by CT angiography.
3-Mosieri J, Chintala K, Delius RE, Walters HL 3rd, Hakimi M.(2004) Abnormal origin of the right subclavian artery from the right pulmonary artery in a patient with D-transposition of the great vessels and left juxtaposition of the right atrial appendage an unusual anatomical variant.
4-Pena E, Nguyen ET, Merchant N, Dennie C (2009) ALCAPA syndrome not just a pediatric disease.
5-Yua J, singh R, Halpern EJ, Fischman D (2011) anomalous origin of the left coronary artery from the pulmonary artery.
6-Atik E, Tanamati C, Kajita L, Babero-Marcial M (2006) unilateral pulmonary artery agenesis.
7-Deutsch MA, Thieme SF, Hinterseer M, (2010) adult presentation of combined unilateral atresia of the right proximal pulmonary artery and left patent ductus arteriosus.
- Cardiac Surgery
- Interventional Cardiology | Cardiovascular Diseases & Vascular Heart Diseases | Cardiac & Cardiovascular Research | Cardiac and Heart Regeneration
Session Introduction
Dalip Sethi
Cesca Therapeutics Inc., USA
Title: Clinical Applications of Autologous Bone Marrow Derived Cells
Biography:
To be Updated Soon...
Abstract:
Cardiovascular Diseases are a major burden on healthcare in modern society. Diseases, such as Critical Limb Ischemia (CLI), are debilitating. Many of the cardiovascular ischemic disease patients have limited surgical or medical options. Regeneration of vascular system is an attractive treatment strategy and is actively pursued in various preclinical and clinical settings. One of the options in regenerative medicine is the use of autologous bone-marrow concentrate (aBMC) containing stem & progenitor cells. Autologous bone-marrow concentrate (aBMC) is derived from the bone marrow aspirate (BMA) by density centrifugation and can be delivered either intra-muscularly (IM) or intra-coronary in the affected region. The aBMC consists of a) an acellular fraction comprised of autologous plasma and the cytokines & b) Cellular Fraction which is a source of (i) proangiogenic cells such as hematopoietic stem cells, mesenchymal progenitor cells, and endothelial progenitor cells; (ii) other cells of immune system at different levels of maturity and multi-potency. The acellular and cellular components participate in tissue repair and regeneration and have made aBMC an attractive source of cells and cytokines for therapeutic angiogenesis in the treatment of ischemic diseases.
Recent Publications
1. Ponemone et al (2017) Safety and Effectiveness of Bone Marrow Cell Concentrate in the Treatment of Chronic Critical Limb Ischemia Utilizing a Rapid Point-of-Care System. Stem Cell International 18: 1-16.
2. Sanghi et al (2016) The Autologous bone marrow concentrate enriched in progenitor cells — an adjuvant in the treatment of acute myocardial infarction. International Journal of Cardiovascular Academy 2: 77-83.
3. Ponemone et al (2016) Enhancement of Atrophic Non-Union Fracture Healing Using Autologous Progenitor Cell-Rich Bone Marrow. HSOA Journal of Stem Cells Research, Development & Therapy. 3: 007.
4. Sanders et al (2013) Effects of Hypoxanthine Substitution in Peptide Nucleic Acids Targeting KRAS2 Oncogenic mRNA Molecules: Theory and Experiment. J. Phys. Chem. B 117(39): 11584-11595.
Sethi et al (2012) Receptor-specific peptides for targeting of liposomal, polymeric, and dendrimeric nanoparticles in cancer diagnosis and therapy. Current Molecular Imaging, 1(1): 3-11
Clifford M. Thornton
Cardiovascular Device & Imaging Marketing Consultant & Medical Journalist, USA
Title: The Future of Cardiology (2018-2030): Advanced Treatments to Combat the Global Advance of Cardiovascular Diseases

Biography:
Clifford Thornton, Cardiovascular Device & Imaging Consultant & Medical Journalist: Graduated from Sanford-Brown Institute, Iselin, NJ with a certification in Cardiovascular Technology, 2004 (emphasis on echocardiography & cardiac pathologies), B.S. Business Admin./Marketing, New York University, Stern School of Business, 1997. Professional experience as a Program Manager with Lucent Technologies/Avaya, Inc. (Enterprise Networking) and led a custom market research practice as a Sr. Analyst for a Telecommunications Industry Research Firm & Consultancy.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: The incidence of Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) is rising globally, and rapidly. As a result, this is not just a health issue, but an economic one as related costs are ballooning to economically unsustainable levels. For example, in the U.S., total healthcare expenditures, which are significantly driven by heart disease, are nearing 20% of the total gross domestic national product (GDP). As developing economies experience similar increases in CVDs, it will become more challenging to meet their populations’ health needs while sustaining their economies. Some of the key related statistics:
- On a worldwide basis, 17.7 Million people died from CVDs in 2015; this accounts for 31% of all global deaths
- The total global cost of treating CVDs was $863 Billion in 2010; this is projected to reach approximately $1,100 Billion by 2030
- 84 Million people in the U.S. suffer from some form of CVD
- 15.8 Million Americans have Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- Heart Failure affects 5 Million U.S. adults
- Heart disease & stroke account for approximately $320 Billion of direct healthcare costs per year in the U.S.
My presentation will address the following key questions and issues:
-
What is the current “Gold Standard” of care today for each of these heart conditions and what are the 3 leading evolving technologies & related treatments to address these heart diseases through 2030:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
- Heart Failure
- Heart Valve Disease
- Cardiac Arrhythmias
- Congenital Heart Defects
- What are the leading medical device companies in each of these areas, what are their product roadmaps, and what evolving and advanced technologies are driving these product strategies? When will we see some of these medical breakthroughs integrated into routine practice?
- Preventive Cardiology: What are some practical, proven, and duplicable?
Recent Publications
“Cardiac Stem Cell Therapies: The Next Revolution in Heart Failure Treatment”, BioInformant, March 14, 2017
Link: https://www.bioinformant.com/cardiac-stem-cell-therapies/
“NYU Stern Innovators – Alumni Paving the Way to the Future in Energy Monitoring & Management and Digital Media Software”, Global Innovation Magazine, February 2017 – Issue 10, pg. 20
Link:http://www.globalinnovationmagazine.com/magazine/feb2017/
What's the BIG DEAL about Diastolic Dysfunction? Here's What....”, LinkedIn – Pulse, October 14, 2016
Link: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/whats-big-deal- diastolic-dysfunction-heres-what-clifford-thornton
"A Fantastic Vessel-Clearing Innovation", Inventor's Digest, February 2016 Issue, pg. 19
Link:https://issuu.com/inventorsdigest/docs/inventorsdigestfebruary2016__1_
"A Totally New Healthcare System", Modern Health Talk, February 17, 2012
Link: http://www.mhealthtalk.com/new-healthcare-system/
Wu Na
Shengjing Hospital of China Medical Universtiy, China
Title: Acute blood glucose fluctuation enhances apoptosis of rat vascular endothelial cell in vivo

Biography:
Wu Na works in Shengjing hospital of China Medical Universtiy. And now she is studying in Cardiovascular Research Center of Lewis Katz School of Medicine in Temple Univeistiy as a vistiting scholar for one .year. Wu Na has her expertise in pathological and metabolic changes in cardiovascular diseases.Her researches focus on investigating the effect and underlying mechanism of metabolic disorder on 1) Atherosclerosis and vascular inflammation, 2) Endothelial function. She goes into rather rigorous surgery techniques in order to established a rat model of acute blood glucose fluctuations and aimed at further investigating the mechanisms underlying increased apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells in the condition.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: Compared to persistent hyperglycemia, fluctuant hyperglycemia has more potential to increase microvascular lesions and the risk of death. In the condition of stress, the glucose levels of those with normal metabolic function may be very high. In this case given hypoglycemic therapy, there may be glucose decreases sharply in the hypoglycemic process, leading to acute glucose fluctuations. Chronic hyperglycemia in vivo and in vitro studies showed that fluctuant hyperglycemia could increase the apoptosis of endothelial cells. But to date, few studies have been conducted to investigate the influence of acute fluctuant hyperglycemia on endothelial cells in vivo. Methodology & Theoretical Orientation: In the present study, an in vivo model of acute fluctuant hyperglycemia was successfully established. We examin the influence of acute fluctuant hyperglycemia and persistent hyperglycemia on vascular endothelial cell apoptosis, oxidative stress and inflammation in vivo. Rats were assigned to three different groups (n=8/group) that received 48-h infusions of saline (SAL group), continuous 50% glucose (constant high glucose group [CHG]), or intermittent 50% glucose (acute blood glucose fluctuation group [AFG]). Expression of related protein and mRNAs were measured in endothelial homogenates prepared from endothelial cells harvested from the aorta Findings: Endothelial cells apoptosis were observed significantly in the aortas of the AFG group. The AFG had reduced Bcl-2 levels and enhanced Bax mitochondrial translocation levels in comparison with the CHG group (P <0.05). Compared with SAL and CHG, AFG increased MDA and 8-isoprostaglandin levels in plasma, oxidative stress in vascular endothelial cells, and inflammatory cytokines in plasma and vascular endothelial cells (P <0.05). Conclusion & Significance:Acute glucose fluctuation could cause significant oxidative stress and inflammation in endothelial cells, and elevate endothelial cell apoptosis, resulting in severe cardiovascular injury. Therefore, not only lowering blood glucose, but also reducing glucose fluctuation is very important in clinic.
Recent Publications
1. Wu N, Shen H, Liu H, et al.(2016) Acute blood glucose fluctuation enhances rat aorta endothelial cell apoptosis, oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression in vivo. Cardiovascular Diabetology, 15:109.
2. Wu N, Lu Y, He B, et al. (2010) Taurine prevents free fatty acid-induced hepatic insulin resistance in association with inhibiting JNK1 activation and improving insulin signaling in vivo. Diabetes Research & Clinical Practice, 90:288-96.
3. Shen H, Wu N, Liu Z, et al. (2017) Epigallocatechin-3-gallate alleviates paraquat-induced acute lung injury and inhibits upregulation of toll-like receptors[J]. Life Sciences, 170:25-32.
4. Shen H, Wu N, Wang Y, et al. (2017) Chloroquine attenuates paraquat-induced lung injury in mice by altering inflammation, oxidative stress and fibrosis.[J]. International Immunopharmacology, 46:16.
5. Shen H, Wu N, Wang Y, et al. (2017) MyD88 gene knockout attenuates paraquat-induced acute lung injury.[J]. Toxicology Letters, 269:41
Larissa Oliveira
Institute of Radioprotection and Dosimetry, Brazil
Title: Radiation Dose and Circulatory Diseases associated with CT Cardiac Angiography (CCTA)

Biography:
Larissa Oliveira is an excellent research scientist who is doing important work in the Medical Physics field - Diagnostic Radiology, Radiation Protection, Dosimetry, Quality Control and Optimization in Brazil. Her researches provided us information regarding about the importance of justification and optimization and the necessity of developing Optimization Programs, as well as the potential of dose reduction for patients without compromise the diagnostic information and the importance of regular education and training. Recently, she studies the impact of the ionization radiation heart injuries during the CT Cardiac angiography. The heart is considered a late response organ. In high doses of radiation, the cardiac effects are already known, though there is no evidence that the cardiovascular system may also be injured by ionizing radiation at low doses. This approach demonstrated the importance to keep the radiation exposure as low as reasonably achievable strategy to reduce the potential risk.
Abstract:
Statement of the Problem: CT Cardiac angiography is increasingly utilized for the noninvasive assessment of coronary artery disease (CAD) due its ability to exclude or diagnose CAD with high accuracy and fast acquisition time. CT delivers high radiation doses to organs that are in the direct path of radiation beam. Thus, there is a potential risk of inducing cellular damage or radiation-induced cancer due to exponentially increased use of this technique in medicine. Exposure of the heart to high doses of ionizing radiation is associated with cardiac lesions, but there are no conclusive studies regarding ionization radiation at low doses and the risks involved for CT Cardiac angiography. The purpose of this study is to review the literature describing the effect of radiation dose on the circulatory system, with emphasis on the heart during the CCTA procedures. Methodology: The research was carried out in a Private Hospital, which has one GE Discovery dual-energy CT scanner. A sample of patients (n= 100) were selected randomly and in each patient, technical parameters and radiation dose were recorded by database. This study was divided in two phases: (1) To evaluate the CT doses using values reported on the equipment console (2) To determine the organ dose using 3D heart with Anthropomorphic Torso Phantom and dosimeter thermoluminescence. Findings: The results demonstrated the median effective dose was similar with the recent studies, approximately 4.6mSv. The second stage (absorbed dose in the heart) is still in progress due to the discrepancy of the values found in this study with the values of the literature.
Conclusion & Significance: The preliminary results demonstrated the importance to record the radiation exposure during the CCTA. Training and improvement of the team involved in the exam to be familiar with the radiation dose received by the patients during clinical practice.
Recent Publications
- Einstein AJ, Elliston CD, Groves DW, Cheng B, Wolff SD, Pearson GDN, Peters MP et al (2012) Effects of Radiation Exposure from Cardiac Imaging: How Good Are the Data? Am Coll Cardiol 59(6): 553-565.
Figure 1. Experimental scheme of the 3D heart positioning in the phantom.
- Hashim S, Karim MKA, Bakar KA, Sabarudin A, Chin AW, Saripan MI, Bradley DA (2016) Evaluation of organ doses and specific k effective dose of 64-slice CT thorax examination using an adult anthropomorphic phantom. Rad. Physics and Chemistry 126:14-20.
- Smith-Bindman R, Lipson J, Marcus R, Kim KP, Mahesh M, Gould R, Berrington de González A, Miglioretti DL (2009) Radiation dose associated with common computed tomography examinations and the associated lifetime attributable risk of cancer. Arch Intern Med. 69(22):2078-86.
- Tahvonen P, Oikarinen H, Pääkkö E, Karttunen A, Blanco Sequeiros R and Tervonen O (2013) Justification of CT examinations in young adults and children can be improved by education, guideline implementation and increased MRI capacity. Br J Radiol. 86:1-9.
- Boerma M, Sridharan V, Mao XW, Nelson GA, Cheema AK, Koturbash, Singh SP, Tackett AJ, Hauer-Jensen M (2016) Effects of ionizing radiation on the heart. Mutat Res. 770:319-327
- Kataria B, Sandborg M, Althén JN (2016) Implications of patients centring on organ in Computed Tomography. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 169(1-4):130-5.
Boerma M, Sridharan V, Mao XW, Nelson GA, Cheema et al (2016) Effects of ionizing radiation on the heart. Mutation Res. 770:319-327
Bi-Hua Tan
Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, USA
Title: Na channel dysfunction in inherited arrhythmias: the effect of common polymorphism, splice variant and intracellular acidosis

Biography:
Bi-Hua Tan was initially trained as a cardiologist in China after graduated from medical school. Then she joined the arrhythmia and clinical electrophysiological study group at Cardiovascular Division, Hyogo College of Medicine in Japan and obtained her PhD degree there. After that she completed her postdoctoral training at the Cellular and Molecular Arrhythmia Research Program, Department of Medicine, University of Wisconsin-Madison. She was the first to characterize the molecular phenotype of eight common polymorphisms and some genetic basis of disease causing mutations in cardiac Na channel. She also first characterized a marked gain of functional KATPKir6.1 channel mutation in KCNJ8 as a novel pathogenic mechanism for the phenotypic expression of both Brugada syndrome and early repolarization syndrome. She was awarded American Heart Association (AHA) Postdoctoral Fellowship and the American Heart Association National Center Scientist Development Grant.
Abstract:
The gene SCN5A on chromosome 3 encodes the α-subunit of the voltage-gated cardiac sodium channel (hNav1.5) that is responsible for large peak inward sodium current (INa) and late INa. Peak INa underlies excitability and conduction in working myocardium (atrial and ventricular cells) and special conduction tissues (Purkinje cells etc.). Late INa influences repolarization and refractoriness. The importance of INa for normal cardiac electrical activity is emphasized by the occurrence of potentially lethal arrhythmias in the setting of inherited and acquired Na channel diseases. SCN5A in humans has two splice variants, one lacking a glutamine at position 1077 (Q1077del) and one containing Q1077. Common sequence variants ("polymorphisms") have also been implicated as risk factors in multiple diseases. Mutations in the cardiac Na channel gene SCN5A cause loss-of-function or gain-of-function and underlie arrhythmia syndromes, such as Brugada syndrome, cardiac conduction disorder, congenital sick sinus syndrome, idiopathic ventricular fibrillation, sudden infant death syndrome, the type 3 long QT syndrome etc. Here, 3 unrelated inherited arrhythmia cases will be presented to show that the loss-of-function or gain-of-function biophysical phenotypes for sodium channel mutations depend on the splice variant background in which it is expressed and the intracellular acidosis, and is also modulated by common polymorphism.
Recent Publications
- Hu RM*, Tan BH*, Tester DJ, Song C, He Y, Dovat S, Peterson BZ, Acherman MJ, Makielski JC (2015) Arrhythmogenic biophysical phenotype for SCN5A mutation S1787N depends upon splice variant background and intracellular acidosis. PLoS ONE. Apr 29: 10(4):e0124921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124921. eCollection
- Hu RM, Tan BH, Orland KM, Valdivia CR, Peterson A, Pu J, Makielski JC (2013) Digenic inheritance novel mutations in SCN5a and SNTA1 increase late INa contributing to LQT syndrome. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. Apr: 304(7):H994-H1001.
- Tester DJ*, Tan BH*, Medeiros-Domingo A, Song C, Makielski JC, Ackerman MJ (2011) Loss-of-Function Mutations in the KCNJ8-Encoded Kir6.1 KATP Channel and Sudden Infant Death Syndrome. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 4:510-515.
- Medeiros-Domingo A*, Tan BH*, Crotti L*, Tester DJ, Eckhardt LL, Cuoretti A, Kroboth SL, Song C, Zhou Q, Kopp D, Schwartz PJ, Makielski JC, Ackerman MJ (2010) Gain-of-Function Mutation, S422L, in the KCNJ8-Encoded Cardiac KATP Channel Kir6.1 as a Pathogenic Substrate for J Wave Syndromes. Heart Rhythm. 7:1466-1471.
- Tan BH, Pundi KN, Van Norstrand DW, Valdivia CR, Tester DJ, Medeiros-Domingo A, Makielski JC. Ackerman MJ (2010)
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome-Associated Mutations in the Sodium Channel Beta Subunits. Heart Rhythm. 7(6):771-778.
- Medeiros-Domingo A*, Tan BH*, Iturralde-Torres P, Tester DJ, Tusié-Luna T, Makielski JC. Ackerman MJ (2009) Unique mixed phenotype and unexpected functional Effect revealed by novel compound heterozygosity mutations involving SCN5A. Heart Rhythm. 6(8):1170-1175.
- Tan BH, Iturralde-Torres P, Medeiros-Domingo A, Nava S, Tester DJ, Valdivia CR, Tusié-Luna T, Ackerman MJ, Makielski JC (2007) A novel C-terminal truncation SCN5A mutation from a patient with sick sinus syndrome, conduction disorder and ventricular tachycardia. Cardiovascular Research. 76:409-417.
- Tan BH, Valdivia CR, Song C, Makielski JC (2006). Partial expression defect for the SCN5A missense mutation G1406R depends upon splice variant background Q1077 and rescue by mexiletine. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 291: H1822- H1828.
- Tan BH,, Valdivia CR, Rok BA, Ye B, Ruwaldt KM, Tester DJ, Ackerman MJ, Makielski JC (2005) Common human SCN5A polymorphisms have altered electrophysiology when expressed in the Q1077 splice variants. Heart Rhythm. 2(7): 741-747.
Ajeya N Ukadgaonkar
Poona Hospital and Research Centre, India
Title: Plasma cyclophilin A : An emerging biomarker of coronary artery disease.

Biography:
Ajeya N Ukadgaonkar is pursuing a superspeciality course (DNB) in Cardiology in Poona Hospital and Research Centre, India. He has completed his MD in Internal Medicine and has worked as an assistant professor in Internal Medicine. He has 2 publications in international and 1 publication in a national journal to his name. He bears a special interest in the field of research.
Abstract:
Background : Cyclophilin A (CyPA) is a protein released from vascular smooth muscle cells in response to reactive oxygen species and serves as a marker of oxidative stress and inflammation, which play an important role in atherosclerosis. We tested the correlation of plasma CyPA levels with coronary artery disease (CAD) and its risk factors.
Methods and Results : Plasma CyPA levels were tested in 205 consecutive patients undergoing coronary angiography (CAG) by immunoassay based sandwich technique and were correlated with CAG results and traditional risk factors for CAD. The data was analyzed using Kruskal Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests. We observed that the median CyPA levels were significantly higher in patients with obstructive CAD (11.8 ng/ml with inter quartile range (IQR) of 9.9 - 16 ng/ml), as compared to non obstructive CAD (8.6 ng/ml with IQR of 7.55 - 9.65 ng/ml) and normal coronaries (5.6 ng/ml with IQR of 4.5 - 6.9 ng/ml ) with p value <0.001. The median CyPA levels were significantly higher in patients with diabetes mellitus (11.5 ng/ml in diabetic versus 9 ng/ml in non diabetic patients, p<0.001), males (10 ng/ml in males versus 7.9 ng/ml in females, p<0.001), smokers (10.6 ng/ml in smokers versus 9.2 ng/ml in non smokers, p=0.008) and post menopausal state (8.8 ng/ml in post menopausal women versus 5.2 ng/ml in pre menopausal women, p=0.005). Statistically significant difference was not found in median CyPA levels with other risk factors such as age, hypertension, dyslipidemia and family history.
Conclusion : CyPA is a strong predictor and emerging biomarker of CAD and an easy, reproducible tool to screen the patients with CAD or suspected CAD.
Keywords : Coronary artery disease, Coronary Angiography, Cyclophilin A, Risk factors.
Recent Publications
- Kimio Satoh (2015) Cyclophilin A in Cardiovascular Homeostasis and Diseases. Tohoku journal of experimental medicine 235(1):1-15.
- Ramachandran et al (2014) Plasma level of cyclophilin A is increased in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and suggests presence of vascular disease. Cardiovascular diabetology 13:38.
- Satoh K, Fukumoto Y, Sugimura K, Miura Y, Aoki T, Nochioka K et al (2013) Plasma cyclophilin A is a novel biomarker for coronary artery disease. Circulation journal 77(2) : 447 –55.
- Nigro P., Satoh K., O’Dell M.R., Soe N.N., Cui Z., Mohan A (2011) Cyclophilin A is an inflammatory mediator that promotes atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Journal of experimental medicine 208(1) : 53-66.
- Satoh K, Shimokawa H, Berk BC (2010) Cyclophilin A: Promising new target in cardiovascular therapy. Circulation journal 74(11) : 2249 –56.
- Satoh K, Matoba T, Suzuki J, O’Dell MR, Nigro P, Cui Z et al (2008) Cyclophilin A mediates vascular remodeling by promoting inflammation and vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Circulation 117(24) : 3088 –98.
Maryam Hadibarhaghtalab
Shiraz University of Medical Sciences, Shiraz, Iran
Title: Defining a BMI cut-off point for the Iranian population: The shiraz heart study

Biography:
Maryam Hadibarhaghtalab has her expertise in evaluation of cardiovascular risk factors and making new cut off and new model for anthropometric indices. She is also trying to make new method and formula to predict cardiovascular events such as metabolic sx,stent restenosis,and even cardiac surgeries and et al .moreover she is the medical author of almost 10 books including biomimicry, innovations in medical sciences and et al. besides she has had MPH degree along with being the top student in general practitioner duration and she is
Abstract:
In this study we evaluated and redefined the optimum body mass index (BMI) cut-off point for the Iranian population based on metabolic syndrome (MeS) risk factors. We further evaluated BMI cut-off points with and without waist circumference (WC) as a cofactor of risk and compared the differences. This study is part of the largest surveillance programs conducted in Shiraz, Iran, termed the Shiraz Heart study. Our study sample included subjects between the ages of 20 to 65 years old. After excluding pregnant women, those with missing data and those with comorbid disease, a total of 12283 made up the study population. The participants underwent a series of tests and evaluations by trained professionals in accordance with WHO recommendations. Hypertension, abnormal fasting blood sugar (FBS), triglyceride (TG) and high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) (in the context of the definition of metabolic syndrome) were prevalent among 32.4%, 27.6%, 42.1 and 44.2% of our participants, respectively. Women displayed higher rates of overall obesity compared to men (based on the definition by the WHO as higher than 30 kg/m2). Regarding MeS, 38.9% of our population had the all symptoms of MeS which was more prevalent among women (41.5% vs. 36%). When excluding WC in the definition of MeS, results showed that males tend to show a higher rate of metabolic risk factors (19.2% vs. 15.6%). Results of multivariate analysis showed that parallel to an increase in BMI, the odds ratio (OR) for acquiring each component of the metabolic syndrome increased (OR = 1.178; CI: 1.166–1.190). By excluding WC, the previous OR decreased (OR = 1.105; CI: 1.093–1.118). Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve analysis showed that the optimum BMI cut-off point for predicting metabolic syndrome was 26.1 kg/m2 and 26.2 kg/m2 [Accuracy (Acc) = 69% and 61%, respectively)] for males and females, respectively. The overall BMI cut-off for both sexes was 26.2 kg/m2 (Acc = 65%) with sensitivity and specificity of 69% and 62%, respectively. This cut-off had a positive predictive value of 54% and a negative predictive value of 76%. When we excluded waist circumference, the optimum BMI cut-off for acquiring metabolic risk factors in males decreased to 25.7 kg/m2(Acc = 67%) and increased for women to 27.05 kg/m2 (Acc = 66%). Iranians are at higher risks of morbidity related to metabolic factors at a lower BMI cut-off and prompt action and preventive health policy are required to prevent and educate Iranians regarding diseases associated with obesity.
Recent publications
1.Freedman DS, Thornton JC, Pi-Sunyer FX, Heymsfield SB, Wang J, Pierson RN, et al. The body adiposity index (hip circumference÷ height1. 5) is not a more accurate measure of adiposity than is BMI, waist circumference, or hip circumference. Obesity. 2012.
2.Despres JP, Lemieux I, Bergeron J, Pibarot P, Mathieu P, Larose E, et al. Abdominal obesity and the metabolic syndrome: contribution to global cardiometabolic risk. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 2008;28(6):1039–49. Epub 2008/03/22. pmid:18356555.
3.Canoy D. Coronary heart disease and body fat distribution. Current atherosclerosis reports. 2010;12(2):125–33. Epub 2010/04/29. pmid:20425248.
4-de Koning L, Merchant AT, Pogue J, Anand SS. Waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio as predictors of cardiovascular events: meta-regression analysis of prospective studies. Eur Heart J. 2007;28(7):850–6. Epub 2007/04/04. pmid:17403720.
5-Melmer A, Lamina C, Tschoner A, Ress C, Kaser S, Laimer M, et al. Body Adiposity Index and other indexes of body composition in the SAPHIR study: association with cardiovascular risk factors. Obesity. 2013;21(4):775–81. pmid:23712981
6- Famodu AA, Awodu OA. Anthropometric indices as determinants of haemorheological cardiovascular disease risk factors in Nigerian adults living in a semi-urban community. Clinical hemorheology and microcirculation. 2009;43(4):335–44. Epub 2009/12/10. pmid:19996522.
